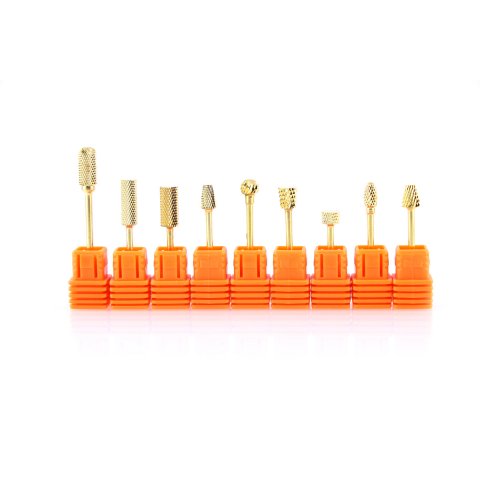
Cemented carbides are extremely hard and wear-resistant materials that are used in a wide range of industrial and manufacturing applications. These materials are composed of tungsten carbide particles that are held together by a metal binder, typically cobalt or nickel.
One of the key advantages of cemented carbides is their ability to be attached or embedded onto various tools and equipment for increased wear resistance and durability. In this article, we will explore the different methods and techniques used for the attachment of cemented carbides.
One of the most common methods for attaching cemented carbides is through brazing. Brazing involves melting a metal alloy, typically silver or copper, onto the surface of the cemented carbide and onto the substrate material. As the alloy cools, it solidifies and forms a strong bond between the two materials.
Another method is through mechanical clamping. This involves the use of specially designed clamps or retaining rings, which apply pressure and hold the cemented carbide in place on the substrate. This method is simple and effective, but may not be suitable for all applications.
Adhesive bonding is another method that is commonly used for the attachment of cemented carbides. This involves the use of an epoxy or other adhesive material that is applied to both the cemented carbide and the substrate. The two materials are then pressed together and allowed to cure. This method can be effective but may not be appropriate for high-stress applications.
Finally, newer technologies are emerging using laser or arc welding to attach carbide nozzles to the steel backing.
In addition to these methods, recent advances have led to the development of specialized tool coatings, such as thermal spray coatings, that can further enhance the wear resistance of cemented carbides. These coatings are applied by heating the substrate and then spraying a ceramic or metal powder onto the surface.
In conclusion, the attachment of cemented carbides is a crucial aspect of their use in various industrial and manufacturing applications. The method chosen for attachment will depend on factors such as the type of substrate, the level of stress that will be placed on the carbide, and the desired level of wear resistance. By carefully selecting the attachment method and utilizing the latest technology, it is possible to achieve excellent results and significantly increase the lifespan of equipment and tools.



 Product review video:
Product review video: